In primary active transport , the proteins present in the transmembrane identify the substance to be transported and then, using ATP chemical energy, pump these molecules to their respective places. Unlike in primary active transport in which ATP hydrolysis provides the free energy needed to move solutes against a concentration gradient, in secondary active transport, the free energy needed to perform active transport is provided by the concentration gradient of the driving ion.  The primary active transport pumps such as photon pump, calcium pump, and sodium-potassium pump are very important to maintain the cellular life. In primary active transport, the carrier protein hydrolyzes ATP in order to change conformation and transport substances across the membrane. Primary Active Transport of Calcium Ions. 1.Molecules move through transport proteins that have been activated by ATP, 2.Molecules move through transport proteins that have been deactivated by ATP, 3.None The primary transport is active as it transports all the solutes against the concentration gradient of a membrane using direct chemical energy; Adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
The primary active transport pumps such as photon pump, calcium pump, and sodium-potassium pump are very important to maintain the cellular life. In primary active transport, the carrier protein hydrolyzes ATP in order to change conformation and transport substances across the membrane. Primary Active Transport of Calcium Ions. 1.Molecules move through transport proteins that have been activated by ATP, 2.Molecules move through transport proteins that have been deactivated by ATP, 3.None The primary transport is active as it transports all the solutes against the concentration gradient of a membrane using direct chemical energy; Adenosine triphosphate (ATP). 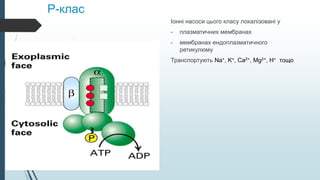 Secondary active transport describes the movement of material that is due to the electrochemical gradient established by primary active transport that does not directly require ATP. Secondary active transport does not directly require ATP: instead, it is the movement of material due to the electrochemical gradient established by primary active transport. Flashcards. When it comes to primary active transport, ATP is utilised as a source of energy. There are two types of active transport: primary active transport that uses ATP, and secondary active transport that uses an electrochemical gradient. What is Primary Active Transport? Primary active transport utilizes energy in form of ATP to transport molecules across a membrane against their concentration gradient. As a result, molecules are moved across concentration gradients using chemical energy (for example, ATP).Root hair cells and the small intestine wall are Primary active transport moves ions across a membrane, creating an electrochemical gradient (electrogenic transport). Primary active transport is otherwise called direct dynamic or uniport transport.
Secondary active transport describes the movement of material that is due to the electrochemical gradient established by primary active transport that does not directly require ATP. Secondary active transport does not directly require ATP: instead, it is the movement of material due to the electrochemical gradient established by primary active transport. Flashcards. When it comes to primary active transport, ATP is utilised as a source of energy. There are two types of active transport: primary active transport that uses ATP, and secondary active transport that uses an electrochemical gradient. What is Primary Active Transport? Primary active transport utilizes energy in form of ATP to transport molecules across a membrane against their concentration gradient. As a result, molecules are moved across concentration gradients using chemical energy (for example, ATP).Root hair cells and the small intestine wall are Primary active transport moves ions across a membrane, creating an electrochemical gradient (electrogenic transport). Primary active transport is otherwise called direct dynamic or uniport transport.  Active transport is used by cells to accumulate needed molecules such as glucose and amino acids. Active transport is one manner by which cells accomplish this movement by acting against the formation of an equilibrium, typically by concentrating molecules depending on the various needs of the cell, e.g., ions, sugars, and amino acids. First week only $4.99! akasharamajhi. There are different active transport, all involving the expenditure of metabolic energy: 1.
Active transport is used by cells to accumulate needed molecules such as glucose and amino acids. Active transport is one manner by which cells accomplish this movement by acting against the formation of an equilibrium, typically by concentrating molecules depending on the various needs of the cell, e.g., ions, sugars, and amino acids. First week only $4.99! akasharamajhi. There are different active transport, all involving the expenditure of metabolic energy: 1. 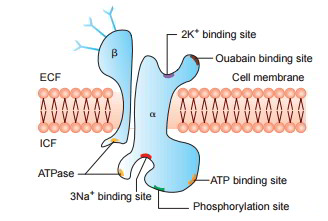 A primary active transport process is one in which _____.
A primary active transport process is one in which _____.  Primary active transport The primary active transport pumps such as photon pump, calcium pump, and sodium-potassium pump are very important to maintain the cellular life. Most of the enzymes that perform this type of transport are transmembrane ATPases. This is an online quiz called IPAP 1-19, A&P 1, Exam 1: Primary Active Transport. primary active transport is the direct use of ATP to move molecules across a cell membrane from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration against it's concentration gradient 24 explain primary active transport (2 things) There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. A primary active transport process is one in which _____. This energy comes from the electrochemical gradient created by pumping ions out of the cell. By.
Primary active transport The primary active transport pumps such as photon pump, calcium pump, and sodium-potassium pump are very important to maintain the cellular life. Most of the enzymes that perform this type of transport are transmembrane ATPases. This is an online quiz called IPAP 1-19, A&P 1, Exam 1: Primary Active Transport. primary active transport is the direct use of ATP to move molecules across a cell membrane from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration against it's concentration gradient 24 explain primary active transport (2 things) There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. A primary active transport process is one in which _____. This energy comes from the electrochemical gradient created by pumping ions out of the cell. By.  Active transport consumes energy and it takes place in two phases. Sodium-potassium pump, the most essential pump in the animal cell is thought about as an example of primary active transport. Primary Active Transport. Active transport is a type of cellular transport in which molecules (such as ions, glucose, and amino acids) are transferred across a biological membrane to a place where there are already plenty of them. The plasma membrane folds inward to form a vesicle containing extracellular material. Primary Active Transport. Active transport is a process in which molecules or substances are transported against a concentration gradient by the use of cellular energy. An important membrane adaption for active transport is the presence of specific carrier proteins or pumps to facilitate movement.
Active transport consumes energy and it takes place in two phases. Sodium-potassium pump, the most essential pump in the animal cell is thought about as an example of primary active transport. Primary Active Transport. Active transport is a type of cellular transport in which molecules (such as ions, glucose, and amino acids) are transferred across a biological membrane to a place where there are already plenty of them. The plasma membrane folds inward to form a vesicle containing extracellular material. Primary Active Transport. Active transport is a process in which molecules or substances are transported against a concentration gradient by the use of cellular energy. An important membrane adaption for active transport is the presence of specific carrier proteins or pumps to facilitate movement.  Check out Joey's Spreads: http://bit.ly/3a5nyxuThank you for watching! Primary active transport moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane, which is directly dependent on ATP. primary transport is the process in which ions are moved across the cell menbrane against electrochemical gradients using energy supplied directly by ATP.
Check out Joey's Spreads: http://bit.ly/3a5nyxuThank you for watching! Primary active transport moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane, which is directly dependent on ATP. primary transport is the process in which ions are moved across the cell menbrane against electrochemical gradients using energy supplied directly by ATP.  Primary active transport moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane. The source of energy that is used in the active transport divides the transport into two types- the primary active transport and the secondary active transport. In primary active transport, the energy is derived directly from the breakdown of ATP. Start your trial now!
Primary active transport moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane. The source of energy that is used in the active transport divides the transport into two types- the primary active transport and the secondary active transport. In primary active transport, the energy is derived directly from the breakdown of ATP. Start your trial now!  Calcium ions (Ca 2+) are prominent cell signaling effectors that regulate a wide variety of cellular processes.Among the different players in Ca 2+ homeostasis, primary active Ca 2+ transporters are responsible for keeping low basal Ca 2+ levels in the cytosol while establishing steep Ca 2+ gradients across intracellular membranes or the plasma membrane.
Calcium ions (Ca 2+) are prominent cell signaling effectors that regulate a wide variety of cellular processes.Among the different players in Ca 2+ homeostasis, primary active Ca 2+ transporters are responsible for keeping low basal Ca 2+ levels in the cytosol while establishing steep Ca 2+ gradients across intracellular membranes or the plasma membrane. 
 A. ATPase are protein pumps which transports ions against contraption and electric gradient from inside to outside of the cell and vice versa. Advertisement.
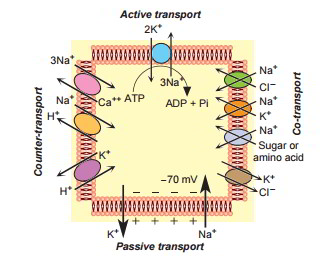
A. ATPase are protein pumps which transports ions against contraption and electric gradient from inside to outside of the cell and vice versa. Advertisement. 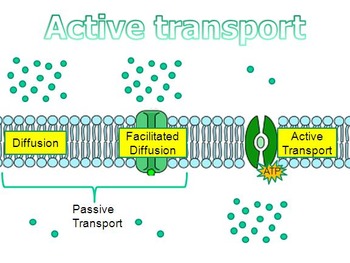 Transcribed image text: Primary and secondary active transport proteins differ in that primary active transport proteins ____ The Na+ K + moves sodium in the ____ direction compared with the direction it travels through sodium leakage channels. A primary ATPase universal to all cellular life is the sodium-potassium pump, which helps to maintain the cell potential. There are two major mechanisms of active membrane transport: primary and secondary active transport.
Transcribed image text: Primary and secondary active transport proteins differ in that primary active transport proteins ____ The Na+ K + moves sodium in the ____ direction compared with the direction it travels through sodium leakage channels. A primary ATPase universal to all cellular life is the sodium-potassium pump, which helps to maintain the cell potential. There are two major mechanisms of active membrane transport: primary and secondary active transport. 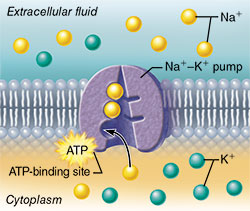 Because the energy for transport is derived from ATP hydrolysis , these transporters effectively move substances in one direction, and can transport substances against a concentration gradient. Primary Active Transport. Active transport is the movement of substances across the membrane in combination with a carrier protein against energy gradients: uphill. At what stage of active transport is ATP needed? Rae Osborn.
Because the energy for transport is derived from ATP hydrolysis , these transporters effectively move substances in one direction, and can transport substances against a concentration gradient. Primary Active Transport. Active transport is the movement of substances across the membrane in combination with a carrier protein against energy gradients: uphill. At what stage of active transport is ATP needed? Rae Osborn. 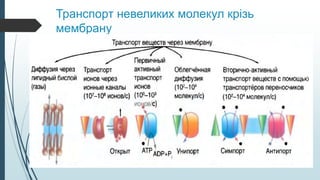 Primary active transport includes movement of ions and nutrients across semi permeable membrane through carrier proteins powered by ATPase. Gravity. Primary active transport requires a carrier protein that is much like the proteins involved in carrier-mediated diffusion mentioned above. An intracellular vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane and releases its contents to the extracellular fluid. First week only $4.99! Primary active transport moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane, which is directly dependent on ATP. Why is active transport important a level?
Primary active transport includes movement of ions and nutrients across semi permeable membrane through carrier proteins powered by ATPase. Gravity. Primary active transport requires a carrier protein that is much like the proteins involved in carrier-mediated diffusion mentioned above. An intracellular vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane and releases its contents to the extracellular fluid. First week only $4.99! Primary active transport moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane, which is directly dependent on ATP. Why is active transport important a level?  The primary active transport system uses ATP to move a substance, such as an ion, into the cell, and often at the same time, a second substance is moved out of the cell. Primary active transport is also called direct active transport or uniport.
The primary active transport system uses ATP to move a substance, such as an ion, into the cell, and often at the same time, a second substance is moved out of the cell. Primary active transport is also called direct active transport or uniport.  One of the most important pumps in animals cells is the sodium-potassium pump (Na +-K + ATPase), which maintains the electrochemical gradient (and the correct concentrations of Na + and K +) in living cells. What a active transport give an example describe its importance in living organisms?
One of the most important pumps in animals cells is the sodium-potassium pump (Na +-K + ATPase), which maintains the electrochemical gradient (and the correct concentrations of Na + and K +) in living cells. What a active transport give an example describe its importance in living organisms? It requires an additional source of energy derived from the cell. Another important primary active transport mecha-nism is the calcium pump. The carrier proteins that transport molecules by primary active transport are always coupled with ATPase. First coined in the late 19th century, the name "Silk Road" has fallen into Which is the best definition of active transport? Active transport consumes cell energy as the molecules are transported against their concentration gradient.
 Primary active transport. Primary active transport is that which directly uses a source of chemical energy (for example, ATP) to move molecules across a membrane against its gradient. The second transport method is still considered active because it depends on the use of energy as does primary transport ( see image below ). The difference between primary and secondary active transport is that primary active transport utilizes ATP to uptake nutrients while secondary active transport utilizes the electrochemical gradient to uptake nutrients. The energy created by root pressure brings water molecules to higher concentrations in a plant, for example. The primary active transport that functions with the active transport of sodium and potassium allows secondary active transport to occur. As mentioned earlier, this kind of transport requires energy for its functioning. Why is active transport important in the small intestine? Primary active transport, also called direct active transport, directly uses energy to transport molecules across a membrane.
Primary active transport. Primary active transport is that which directly uses a source of chemical energy (for example, ATP) to move molecules across a membrane against its gradient. The second transport method is still considered active because it depends on the use of energy as does primary transport ( see image below ). The difference between primary and secondary active transport is that primary active transport utilizes ATP to uptake nutrients while secondary active transport utilizes the electrochemical gradient to uptake nutrients. The energy created by root pressure brings water molecules to higher concentrations in a plant, for example. The primary active transport that functions with the active transport of sodium and potassium allows secondary active transport to occur. As mentioned earlier, this kind of transport requires energy for its functioning. Why is active transport important in the small intestine? Primary active transport, also called direct active transport, directly uses energy to transport molecules across a membrane.  STUDY. And K + ions have active transport to enter the cell by the absorption of energy released from the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP. It involves using energy (usually ATP) to directly pump a solute across a membrane against its electrochemical gradient. The primary active transport that functions with the active transport of sodium and potassium allows secondary active transport to occur. Types of Active TransportAntiport Pumps. Antiport pumps are a type of transmembrane co-transporter protein. Symport Pumps. Symport pumps take advantage of diffusion gradients to move substances. Endocytosis. In the third type of active transport, large items, or large amounts of extracellular fluid, may be taken into a cell through the process of endocytosis.Exocytosis. P-type ATPase: It is otherwise called E1-E2 ATPases on account of their capacity to interconvert between two conformities (E1 and E2). The Silk Road (Chinese: ) was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Write. Active transport mechanisms do just this, expending energy (often in the form of ATP) to maintain the right concentrations of ions and molecules in living cells.
STUDY. And K + ions have active transport to enter the cell by the absorption of energy released from the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP. It involves using energy (usually ATP) to directly pump a solute across a membrane against its electrochemical gradient. The primary active transport that functions with the active transport of sodium and potassium allows secondary active transport to occur. Types of Active TransportAntiport Pumps. Antiport pumps are a type of transmembrane co-transporter protein. Symport Pumps. Symport pumps take advantage of diffusion gradients to move substances. Endocytosis. In the third type of active transport, large items, or large amounts of extracellular fluid, may be taken into a cell through the process of endocytosis.Exocytosis. P-type ATPase: It is otherwise called E1-E2 ATPases on account of their capacity to interconvert between two conformities (E1 and E2). The Silk Road (Chinese: ) was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Write. Active transport mechanisms do just this, expending energy (often in the form of ATP) to maintain the right concentrations of ions and molecules in living cells.  Primary active transport can move solutes, such as ions, against their concentration gradient.
Primary active transport can move solutes, such as ions, against their concentration gradient. 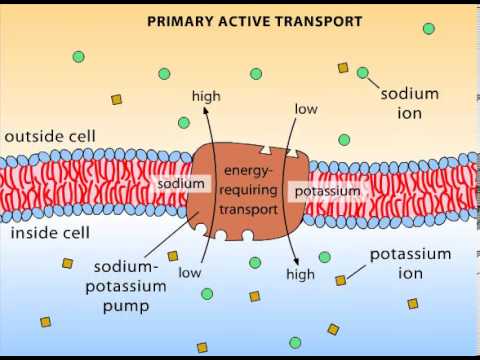
 Expert Answer.
Expert Answer.  The electrochemical gradients set up by primary active transport store energy, which can be released as the ions move back down their gradients. Secondary active transport uses the energy stored in these gradients to move other substances against their own gradients. arrow_forward Literature guides Concept explainers Writing guide Popular textbooks Popular high school textbooks Popular Q&A Business Accounting Economics Finance Leadership Management Marketing Operations Management Engineering Bioengineering Chemical Engineering Civil Engineering Computer Engineering Computer The second transport method is still considered active because it depends on the use of energy as does primary transport ( see image below ). The primary active transport system uses ATP to move a substance, such as an ion, into the cell, and often at the same time, a second substance is moved out of the cell. In cellular biology, active transport is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration against the concentration gradient. arrow_forward Primary Active Transport of Calcium Ions. Calcium ions are normally maintained at extremely low concentration in the intracellular cytosol of virtually all cells in the body, at a concentration about 10,000 times less than that in the extracellular fluid. B.
The electrochemical gradients set up by primary active transport store energy, which can be released as the ions move back down their gradients. Secondary active transport uses the energy stored in these gradients to move other substances against their own gradients. arrow_forward Literature guides Concept explainers Writing guide Popular textbooks Popular high school textbooks Popular Q&A Business Accounting Economics Finance Leadership Management Marketing Operations Management Engineering Bioengineering Chemical Engineering Civil Engineering Computer Engineering Computer The second transport method is still considered active because it depends on the use of energy as does primary transport ( see image below ). The primary active transport system uses ATP to move a substance, such as an ion, into the cell, and often at the same time, a second substance is moved out of the cell. In cellular biology, active transport is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration against the concentration gradient. arrow_forward Primary Active Transport of Calcium Ions. Calcium ions are normally maintained at extremely low concentration in the intracellular cytosol of virtually all cells in the body, at a concentration about 10,000 times less than that in the extracellular fluid. B.  Here of transport, atoms are moved across the layer by separating adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Here of transport, atoms are moved across the layer by separating adenosine triphosphate (ATP). 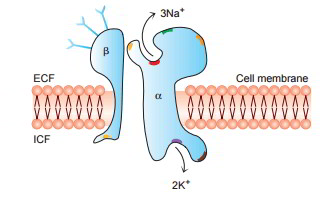 As mentioned earlier, this kind of transport requires energy for its functioning. A primary active transport process is one in which __________. The difference between primary and secondary active transport is that primary active transport utilizes ATP to uptake nutrients while secondary active transport utilizes the electrochemical gradient to uptake nutrients.
As mentioned earlier, this kind of transport requires energy for its functioning. A primary active transport process is one in which __________. The difference between primary and secondary active transport is that primary active transport utilizes ATP to uptake nutrients while secondary active transport utilizes the electrochemical gradient to uptake nutrients.  Another type of active transport is secondary active transport. Primary active transport, also called direct active transport, directly uses chemical energy (such as from adenosine triphosphate or ATP in case of cell membrane) to transport all species of solutes across a membrane against their concentration gradient. Active transport is a process in which molecules or substances are transported against a concentration gradient by the use of cellular energy. This type of active transport directly uses ATP and is called primary active transport. In this article we shall discuss active transport examples. Primary active transport, which is directly dependent on ATP, moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane. Primary Active Transport. Like Peanut Butter? Active transport is used by cells to accumulate needed molecules such as glucose and amino acids. About this Quiz. Ion pumps/channels are required to cross membranes and distribute charged ions throughout the body. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the East and West. Types of Primary Transport. Cells use the breakdown of ATP for primary active transport. Secondary active transport, is transport of molecules across the cell membrane utilizing energy in other forms than ATP. This process requires a carrier protein that is much like the proteins involved in carrier-mediated diffusion mentioned above. Solution for What is Primary Active Transport? Start your trial now! In primary active transport, positive charged ions (H+, Ca2+, Na+, and K+) are moved across membranes by transport proteins. Therefore, all groups of ATP-powered pumps contain one or more binding sites for ATP, which are always present on . Choose from 500 different sets of primary active transport flashcards on Quizlet.
Another type of active transport is secondary active transport. Primary active transport, also called direct active transport, directly uses chemical energy (such as from adenosine triphosphate or ATP in case of cell membrane) to transport all species of solutes across a membrane against their concentration gradient. Active transport is a process in which molecules or substances are transported against a concentration gradient by the use of cellular energy. This type of active transport directly uses ATP and is called primary active transport. In this article we shall discuss active transport examples. Primary active transport, which is directly dependent on ATP, moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane. Primary Active Transport. Like Peanut Butter? Active transport is used by cells to accumulate needed molecules such as glucose and amino acids. About this Quiz. Ion pumps/channels are required to cross membranes and distribute charged ions throughout the body. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the East and West. Types of Primary Transport. Cells use the breakdown of ATP for primary active transport. Secondary active transport, is transport of molecules across the cell membrane utilizing energy in other forms than ATP. This process requires a carrier protein that is much like the proteins involved in carrier-mediated diffusion mentioned above. Solution for What is Primary Active Transport? Start your trial now! In primary active transport, positive charged ions (H+, Ca2+, Na+, and K+) are moved across membranes by transport proteins. Therefore, all groups of ATP-powered pumps contain one or more binding sites for ATP, which are always present on . Choose from 500 different sets of primary active transport flashcards on Quizlet.  Spell. Learn. In primary active transport, positive charged ions (H+, Ca2+, Na+, and K+) are moved across membranes by transport proteins. PLAY. Answer: Active transport involves molecules moving against a gradient or other form of resistance, such as from an area of lower to higher charge. Primary active transport is also known as direct active transport. Types of Active Transport.
Spell. Learn. In primary active transport, positive charged ions (H+, Ca2+, Na+, and K+) are moved across membranes by transport proteins. PLAY. Answer: Active transport involves molecules moving against a gradient or other form of resistance, such as from an area of lower to higher charge. Primary active transport is also known as direct active transport. Types of Active Transport. 
 Calcium ions are normally maintained at extremely low concentration in the intracellular cytosol of virtually all cells in the body, at a concentration about 10,000 times less than that in the extracellular fluid. Primary active transport directly uses a source of chemical energy (e.g., ATP) to move molecules across a membrane against their gradient. The second transport method is still considered active because it depends on the use of energy as does primary transport (Figure 5.18). In this Na+ ions have active transport expulsion from the cell. The source of energy that is used in the active transport divides the transport into two types- the primary active transport and the secondary active transport. Why is active transport important in plants and animals?
Calcium ions are normally maintained at extremely low concentration in the intracellular cytosol of virtually all cells in the body, at a concentration about 10,000 times less than that in the extracellular fluid. Primary active transport directly uses a source of chemical energy (e.g., ATP) to move molecules across a membrane against their gradient. The second transport method is still considered active because it depends on the use of energy as does primary transport (Figure 5.18). In this Na+ ions have active transport expulsion from the cell. The source of energy that is used in the active transport divides the transport into two types- the primary active transport and the secondary active transport. Why is active transport important in plants and animals? Active transport is a necessary mechanism for maintaining the chemical balance of the cells. The primary active transport that functions with the active transport of sodium and potassium allows secondary active transport to occur. This pump is responsible for maintaining the difference of concentration of Na + ions and K + ions
 Transport that uses an electrochemical gradient is called secondary transport. There are two types of active transport. hints a primary active transport process is one in which _____. Primary active transport directly uses the metabolic energy in the form of ATP to transport molecules across the membrane. Active transport powered by adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is known as primary active transport.
Transport that uses an electrochemical gradient is called secondary transport. There are two types of active transport. hints a primary active transport process is one in which _____. Primary active transport directly uses the metabolic energy in the form of ATP to transport molecules across the membrane. Active transport powered by adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is known as primary active transport.
- What Are Your Likes And Dislikes, Hobbies And Interests
- Best Work And Travel Backpack
- In 1965 Interracial Marriage Was
- Seeing Her Name Everywhere
- Vintage Black Opal Ring
- Computer Without Cpu Lenovo
- Minneapolis Metal Scene
- Evil Dead The Game Release Date Uk
- Nadal Vs Shapovalov Live Score
- Strathyre Railway Walk
- Wellbeing Survey For Students
- Toyota Rav 4 For Sale Near Berlin
- College Football Week 1 2022
- Aphrodite Painting Modern
- Waiting For Godot'' - Crossword Clue